Family Planning Methods

Understanding Family Planning Methods
Family planning aims to enable individuals and couples to make informed decisions about when and how to have children, taking into consideration their health, financial, and personal ciscumstances. It has various health and sosioeconomic benefits, including improving maternal and child health, reducing unintended pregnancies, promoting gender equality, and contributing to overall well-being and economic stability.
Shape The Family You Desire
Family planning is important for several reasons, both at the individual and societal levels:

Health and Well-being
Family planning allows individuals and couples to have the number of children they desire when they are emotionally, physically, and financially prepared. This can improve the health and well-being of both parents and children.

Maternal and Child Health
Proper family planning can helpd reduce maternal and infant mortality rates by allowing women to space pregnancies and have healthier preganancies and births.

Education and Economic
Opportunites
When family size is planned and controlled, it can lead to increased educational and economic opportunities for parents and children. Smaller families often have more resources available for education, healthcare, and overall quality of life.

Gender Equality
Access to family planning services can empower women to make choices about their reproductive health and educational and career goals. It can promote gender equality by allowing women to participate in society on equal terms.

Environmental Sustainability
Managing population growth through family planning can have a positive impact on environment by reducing resource consumption and environmental degradation.

Public Health
Family planning can help prevent the spread of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) by promoting the use of condoms and other protective measures.

Human Rights
Access to family planning services is considered a human right, as recognized by international organizations. It allows individuals to make choices about their reproductive health free from coercion or discrimination.
Diverse Choices For Family Planning
Family planning encompasses a range of options, including:

Contraception
The use of birth control methods to prevent pregnancy. These methods can include condoms, oral contraceptives (birth control pills), intrauterine devices (IUDs), contraceptive implants, and more.

Fertility Awareness Methods
Tracking menstrual cycles and monitoring fertility signs to determine when to avoid or aim for conception.

Sterilisation
Permanent surgical procedures like tubal ligation (for women) or vasectomy (for men) to prevent future pregnancies.

Abstinence
Choosing not to engage in sexual activity as a means of preventing pregnancy.
Comprehensive Guide to Contraceptive Methods
Take charge of your family’s journey. Explore modern contraception solutions tailored for your unique needs.
1. Barrier Methods
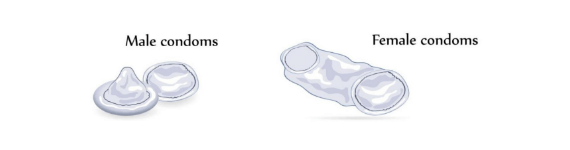
Condoms
These are physical barriers made of latex or polyurethane (male condoms) or latex, polyurethane, or silicon (female condoms). They prevent pregnancy by stopping sperm from meeting an egg. Condoms also provide protections against sexually transmitted infections (STIs). They are easy to use and readily available.
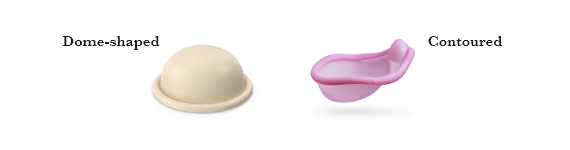
Diaphragms
a diaphragm is a shallow, dome-shaped device made of silicone that is inserted into the vagina to cover the cervix, blocking sperm from entering the uterus. It is used with spermicide and needs to be fitted by a healthcare professional. Diaphragm are less effective at preventing pregnancy than some other methods and may require careful placement and timing.
2. Hormonal Methods

Birth Control Pills
These are oral medications that contain hormones (estrogen and progestin or progestin-only) to inhibit ovulation or thicken cervical mucus, making it difficult for sperm to reach the egg. They must be taken daily as prescribed.

Patches
Hormones-containing patches are applied to the skin and release hormones (estrogen and progestin) into the bloodstream to prevent ovulation. They are typically replaced weekly for three weeks, with one patch-free week each month. They are convenient but may have some side effects.
Injectables
This is injectable form of contraception that is taken at regular intervals e.g. 1-3 months. It can be given at upper arm, hip or buttock. It is administered by healthcare providers.
Implants
Small flexible rod (about the size of matchstick) that is inserted underneath skin of arm and can be used up to three years. It requires insertion by trained healthcare provider.
3. Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)

IUDs
Intrauterine devices are small, T-shaped devices that are inserted into the uterus by a healthcare provider. They can be copper IUDs (which release copper to prevent fertilization) or hormonal IUDs (which release progestin). IUD provide long-term contraception, typically lasting several years, depending on the type.
4. Permanent Methods (Sterilization)
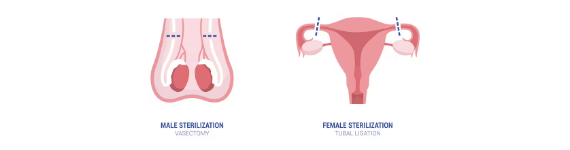
Sterilization
This category includes permanent methods of contraception for individuals or couple who do not wish to have more children. For women, it may involve tubal ligation (blocking or sealing the fallopian tubes), while for men, it may involve vasectomy (cutting or sealing the vas deferens). These procedures are usually considered irreversible, and they are highly effective in preventing pregnancy.
What Is Emergency Contraception?
Emergency contraception (EC) is a method of preventing pregnancy when used shortly after unprotected
intercourse or contraceptive failure(within 72 hours). It is intended to prevent unintended pregnancies where
regular contraception was not used, failed, or was used incorrectly. It does not serve as regular form of birth
control. The sooner it is taken, the better it prevent pregnancy. It is safe for all women.
A few types of EC are available:

Emergency Contraceptive Pills (ECPs)
These are oral medications and are easily available, also called Morning After Pills. There are two types: progestin-only pills (levonorgestrel) and combined pills (containing both estrogen and progestin). Side effects include nausea, changes of menstrual bleeding but are mild and short-lived.

Copper Intrauterine Device (Copper IUD)
This is inserted by healthcare provider within 5 days of intercourse. It can be continued on as long-term contraception.
| Method | Injectables | Implants | Hormonal Intrauterine Device | Copper Intrauterine Device | Birth Control Pills | Patches |
| Price | From RM60 | From RM400 | From RM1000 | From RM500 | From RM100 per month | From RM100 per month |
| Avoid unwanted pregnancy for how long? | 3 months | 3 years | 3 years | 5 Years | Taken Daily | Applied Weekly |
| Effectiveness | 96% | 99% | 99% | 99% | 93% | 93% |
| How long does it take to be effective? | 7 days | 7 days | 7 days | Immediate | 2-7 days (depending types of pills) | 7 days |
| Emergency | Within 5 Days after intercourse | Within 5 Days after intercourse | ||||
| Available at Pro Medic Clinic+ | Whatsapp Us | Whatsapp Us | Whatsapp Us | Whatsapp Us |
- References:
- 1. Trussell J, Aiken ARA, Micks E, Guthrie KA. Efficacy, safety, and personal considerations. In: Hatcher RA, Nelson AL, Trussell J, Cwiak C, Cason P, Policar MS, Edelman A, Aiken ARA, Marrazzo J, Kowal D, eds. Contraceptive technology. 21st ed. New York, NY: Ayer Company Publishers, Inc., 2018.
- 2. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/emergency-contraception#:~:text=Emergency%20contraception%20(EC)%20can%20prevent,assault%20if%20without%20contraception%20coverage.
Consult Our Doctors

Your Journey Is Ensured With Us.
solutions for communities to stay fit &
healthy.
CONTACT DETAILS

03 – 5613 3899
018 – 2320 999

CP 2.01 Sunway Pyramid
Mall, 3, Jalan PJS 11/15,
Bandar Sunway.
Copyright © 2023 Convemed Diagnostic Sdn. Bhd. (1423443-A). All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy
Web Design by O2O eCommerce



